箭头函数
箭头函数是什么
箭头函数的注意事项
this指向
不适用箭头函数的场景
箭头函数的应用
ES6简介
ECMAScript 6
ECMAScript是语言的标准 6是版本号
ES6 = ECMAScript这门语言的第6代标准
ECMAScript
ECMA
欧洲计算机制造商协会
标准化组织
ECMAScript = 由ECMA这个标准化组织制定的一个语言标准
具体是什么
语法
API
js
let name = 'yunmu';
function add(x, y){return x + y;}
//基本数据类型:数字、字符串、布尔值、undefined、null引用数据类型:对象
[1,2,3].push(4);
{}.toString();
parselnt(3.14);
//ECMAScript =语法+API
历史版本
ES1~3、ES5~6
ES4被废弃了
ES3
do while、switch、正则表达式等
ES5
forEach、map、filter、Object.create、Object.defineProperty等
ES6
命名方式
ES6 vs ES2015
ES6->ES7->ES8->...= ES6+
ES2015->ES2016->ES2017->...
ES 与JavaScript的关系
JavaScript(浏览器端) = ECMAScript(语法+API)+ DOM+BOM
ES6的兼容性
主流浏览器的最新版本几乎全部支持ES6
IE老版本等不支持的浏览器,可以用Babel转码
放心大胆地使用ES6
课前回顾
let:声明变量
const:声明常量
const
const声明的是常量
const声明后必须立即初始化
const声明的常量可以修改,但不能重新赋值
let、const 与var的区别
重复声明
变量提升
暂时性死区
window对象的属性和方法(全局作用域中)
块级作用域
块级作用域
有哪些块级作用域:{}、for、while、do while、if、switch
模板字符串
使用反引号`
通过${值}注入
空格、换行或缩进都会被保留在输出之中
特殊字符需要通过 \ 转义 ` \
1.箭头函数初识
- 认识箭头函数
- 箭头函数的结构
- 如何将一般函数改写成箭头函数
1.认识箭头函数
js
const add = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
};
console.log(add(2, 2));
2.箭头函数的结构
const/let 函数名 = 参数 => 函数体
3.如何将一般函数改写成箭头函数
声明形式
js
function add() {}
声明形式->函数表达式形式
js
const add = function () {};
函数表达式形式->箭头函数
js
const add = () => {};
2.箭头函数的注意事项
- 单个参数
- 单行函数体
- 单行对象
1.单个参数
单个参数可以省略圆括号
js
const add = x => {
return x + 1;
};
console.log(add(1));
无参数或多个参数不能省略圆括号
js
const add = () => {
return 1 + 1;
};
const add = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
};
console.log(add(1, 1));
2.单行函数体
单行函数体可以同时省略 {} 和 return
js
const add = (x, y) => {
return x + y;
};
const add = (x, y) => x + y;
// console.log(add(1, 1));
多行函数体不能再化简了
js
const add = (x, y) => {
const sum = x + y;
return sum;
};
3.单行对象
如果箭头函数返回单行对象,可以在 {} 外面加上 (),让浏览器不再认为那是函数体的花括号
js
const add = (x, y) => {
return {
value: x + y
};
};
js
//不加圆括号 会让浏览器以为是函数的花括号
const add = (x, y) => ({
value: x + y
});
4.单行数组
数组化简没问题
js
const add = (x, y) => {
return [x, y];
};
console.log(add(2, 2));
js
const add = (x, y) => [x, y];
console.log(add(30, 20));
3.非箭头函数的this指向
1.全局作用域中的 this 指向
js
console.log(this); // window
2.一般函数(非箭头函数)中的 this 指向
js
function add() {
console.log(this);
}
//只有在函数调用的时候 this 指向才确定,不调用的时候,不知道指向谁
//this 指向和函数在哪儿调用没关系,只和谁在调用有关
//没有具体调用对象的话,this 指向 undefined,在非严格模式下,转向 window
js
add(); // undefined->window(非严格模式下)
window.add(); // 指向window
严格模式下
js
'use strict';
function add() {
console.log(this);
}
add(); //严格模式就指向 undefined
其他情况
js
const calc = {
add: add
};
// calc.add(); // calc
//const adder = calc.add;
//adder(); // undefined->window(非严格模式下)
dom事件绑定
js
document.onclick = function () {
console.log(this);
};
document.onclick(); // document
构造函数
js
function Person(username) {
this.username = username;
console.log(this);
}
const p = new Person('tian'); //this指向实例生成的对象
4.箭头函数的this指向
[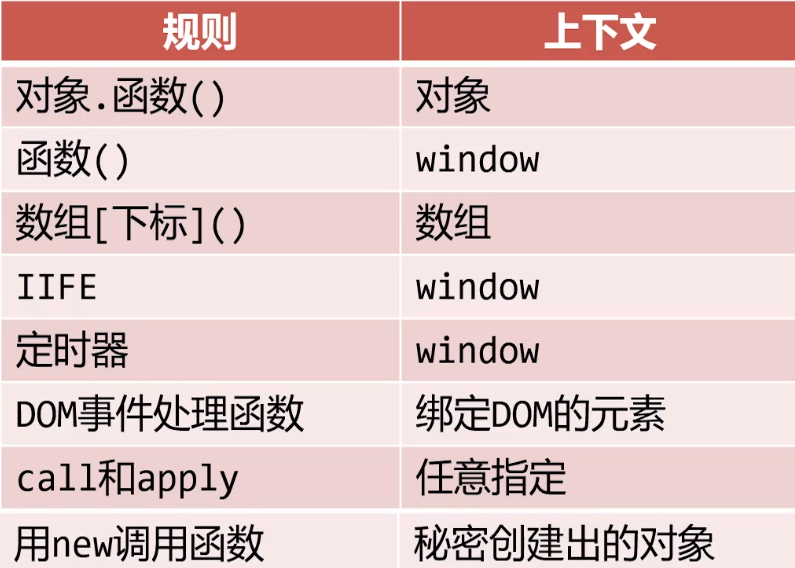
1.箭头函数中的 this 指向
箭头函数没有自己的 this 指向上层作用域的this
js
const calc = {
add: () => {
console.log(this);
}
};
calc.add(); // window
2.练习
js
const calc = {
add: function () {
// this
const adder = () => {
console.log(this);
};
adder();
}
};
// calc.add(); // calc
const addFn = calc.add;
addFn(); // undefined->window
5.不适应箭头函数的场景
- 作为构造函数
- 需要this指向调用对象的时候
- 需要使用arguments的时候
1.作为构造函数
箭头函数没有 this
js
const Person = () => {};
new Person();
2.需要 this 指向调用对象的时候
js
document.onclick = function () {
console.log(this); //document
};
document.onclick = () => {
console.log(this); //window
}
document.addEventListener(
'click',
() => {
console.log(this); //window
},
false
);
3.需要使用 arguments 的时候
箭头函数中没有 arguments
剩余参数可以解决
js
function add() {
console.log(arguments);
}
add(1,2,3,4,5);
js
const add = () => console.log(arguments);
add(1,2);
6.箭头函数的应用
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>箭头函数的应用</title>
<style>
body {
padding: 50px 0 0 250px;
font-size: 30px;
}
#btn {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
margin-right: 20px;
font-size: 30px;
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">开始</button>
<span id="result">0</span>
<script>
const btn = document.getElementById('btn');
const result = document.getElementById('result');
// const timer = {
// time: 0,
// start: function () {
// // this
// var that = this;
// // let self = this;
// btn.addEventListener(
// 'click',
// function () {
// setInterval(function () {
// console.log(this);
// // this.time++;
// // result.innerHTML = this.time;
// that.time++;
// result.innerHTML = that.time;
// }, 1000);
// },
// false
// );
// }
// };
const timer = {
time: 0,
start: function () {
// this
btn.addEventListener(
'click',
() => {
// this
setInterval(() => {
console.log(this);
this.time++;
result.innerHTML = this.time;
}, 1000);
},
false
);
}
};
timer.start();
</script>
</body>
</html>
课程总结
箭头函数是什么
函数的一种简化形式
箭头函数的结构:const/let 函数名 = 参数 => 函数体
改写成箭头函数:声明形式 -> 函数表达式形式 -> 箭头函数
箭头函数的注意事项
单个参数可以省略圆括号
单行函数体可以同时省略 {} 和return
函数体是单行对象,省略 函数{} 和 return 后,需要在对象外面加上()
非箭头函数中的this指向
全局作用域中的this指向window
函数中的this,只有所在函数被调用的时候,才有明确指向
this指向调用其所在函数的那个对象
没有具体调用对象,this指向undefined,在非严格模式下转向window
箭头函数中的this指向
箭头函数没有自己的this
箭头函数中的this是通过作用域链查找的
不适用箭头函数的场景
不适合作为构造函数
不适合需要this指向调用对象的时候
不适合需要使用arguments的时候
 tian~
tian~
