数学对象Math
Math是 JavaScript 的原生对象,提供各种数学功能。该对象不是构造函数,不能生成实例,所有的属性和方法都必须在
Math对象上调用。
js
console.log(Math);
Math.abs()
js
let nums = -55;
console.log(Math.abs(nums));
Math.max(),Math.min()
Math. max()可以得到参数列表的最大值
Math.min()可以得到参数列表的最小值如果参数为空,
Math.min返回Infinity,Math.max返回-Infinity
js
let min = Math.min(5, -4, 0, 9, 108, -55);
console.log(min);//出现一个不是数字或字符串则返回NaN
js
let max = Math.max(88, 0, 6, 47, 199);
console.log(max);
如何利用Math.max()求数组最大值
Math.max()要求参数必须是“罗列出来”,而不能是数组
还记得apply方法么?它可以指定函数的上下文,并且以数组的形式传入“零散值”当做函数的参数
js
let arr = [3, 4, 4, 3, 2, 2, 1, 3, 5, 7, 4, 3];
console.log( Math.max.apply(null, arr) ); // 7
// 在今后学习ES6之后,求数组最大值还可以
console.log( Math.max(...arr) ); // 7
Math.floor(),Math.ceil()
Math.floor向下取整:
Math.ceil向上取整
js
let num = 189.69;
let int1 = Math.ceil(num); //190
js
let num = 189.69;
let int3 = Math.floor(num); //189
Math.round()
Math.round方法用于四舍五入。
js
let num1 = 0.1;
let num2 = 0.5;
console.log(Math.round(num1));//0
console.log(Math.round(num2)); //1
注意,它对负数的处理(主要是对0.5的处理)。
js
Math.round(-1.1) // -1
Math.round(-1.5) // -1
Math.round(-1.6) // -2
//五舍六入
四舍五入到小数点后某位
何时才能实现“四舍五入到小数点后某位”呢?
js
//3.6482 四舍五入到后两位变成 3.65
let a = 3.6482;
console.log(Math.round(a * 100) / 100);
Math.pow()
Math.pow方法返回以第一个参数为底数、第二个参数为指数的幂运算值。
js
Math.pow(2, 2) // 4
// 等同于 2 ** 2
Math.pow(2, 3) // 8
// 等同于 2 ** 3
Math.sqrt()
Math.sqrt方法返回参数值的平方根。如果参数是一个负值,则返回NaN。
js
Math.sqrt(4) // 2
Math.sqrt(-4) // NaN
Math.random()
Math.random()可以得到0~1之间的小数
为了得到[a,b]区间内的整数,可以使用这个公式:
从[a , b]之间取随机整数:
pasreInt(Math.random() * (b - a + 1) + a)
从0~n之间去随机:
Math.floor(Math.random()*(n+1));
js
console.log(Math.random());
console.log(Math.random());
console.log(Math.random());
console.log(Math.random());
// 如果要生成[a, b]之内的整数,就要使用公式
// parseInt(Math.random() * (b - a + 1)) + a
// [3, 8]
console.log(parseInt(Math.random() * 6) + 3);
Math.PI
数学中的 π (圆周率)
360度等于2π
三角函数方法
Math对象还提供一系列三角函数方法。
Math.sin():返回参数的正弦(参数为弧度值) 对边比斜边
Math.cos():返回参数的余弦(参数为弧度值) 临边比斜边
Math.tan():返回参数的正切(参数为弧度值) 对边比临边
Math.asin():返回参数的反正弦(返回值为弧度值)
Math.acos():返回参数的反余弦(返回值为弧度值)
Math.atan():返回参数的反正切(返回值为弧度值)
弧度和角度
360° 等于 2π的弧度
随机概率抽奖
html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
#wrap {
position: relative;
width: 500px;
height: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
border: 1px solid #999;
border-radius: 3px;
font-size: 12px;
}
#wrap .top {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
position: relative;
width: 100%;
border-bottom: 1px dotted pink;
}
#wrap .top input {
width: 100px;
height: 30px;
top: 5px;
right: 5px;
}
#wrap .bottom {
overflow: hidden;
position: relative;
width: 100%;
height: 220px;
}
#wrap .bottom div {
position: absolute;
bottom: 0;
}
.cost,
.win {
align-self: flex-end;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<div class="top">
<p>抽奖:2元抽一次</p>
<p>一等奖:10元 (10%)</p>
<p>二等奖:5元 (10%)</p>
<p>三等奖:2元 (10%)</p>
<p>四等奖: 1元 (20%)</p>
<p>谢谢参与 (50%)</p>
<input type="button" id="btn" value="抽奖一次" />
<p class="cost">总花费<span>0</span></p>
<p class="win">总奖金<span style="color: red">0</span></p>
</div>
<div class="bottom">
<div id="show"></div>
</div>
</div>
<script>
let oBtn = document.getElementById("btn");
let oShow = document.getElementById("show");
let oCost = document.querySelector(".cost span");
let oWin = document.querySelector(".win span");
let costNum = 0;
let winNum = 0;
oBtn.onclick = function () {
let random = parseInt(Math.random() * 100 + 1);
let str = "";
if (random <= 10) {
str = "恭喜获得:一等奖 10元";
winNum += 10;
} else if (random <= 20) {
str = "恭喜获得:二等奖 5元";
winNum += 5;
} else if (random <= 30) {
str = "恭喜获得:三等奖 2元";
winNum += 2;
} else if (random <= 50) {
str = "恭喜获得:四等奖 1元";
winNum += 1;
} else {
str = "谢谢参与☺ 没钱";
}
costNum += 2;
oShow.innerHTML += `<p>${str}</p>`;
oCost.innerHTML = costNum;
oWin.innerHTML = winNum;
};
</script>
</body>
</html>
日期对象Date()
使用new Date()即可得到当前时间的日期对象,它是object类型值
使用new Date(2020,11,1)即可得到指定日期的日期对象,注意第二个参数表示月份,从0开始算,11表示12月
也可以是new Date( ' 2020-12-01'y这样的写法
js
// 什么参数都不加,自动得到今天此时此刻的日期对象
let d1 = new Date();
console.log(d1);
console.log(typeof d1);
设置指定时间
1、单参数(字符串)方法设置
js
let date = new Date( " 2010-12-12 12:12:12 " );
console.log( date ); // Sun Dec 12 2010 12:12:12 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
2、单参数(数字)方法设置
设置 - 格林威治时间1970年01月01日00时00分00秒的时间戳(即 0) + 参数(毫秒数)= 所设置的时间
js
//只有一个参数会认为是毫秒数
let date = new Date( 2000 );
console.log( date ); // Thu Jan 01 1970 08:00:02 GMT+0800 (中国标准时间)
console.log( date.getTime() ) // 2000
3、多参数(数字)方法设置
js
//代表年、月、日、小时、分钟、秒、毫秒
let date = new Date( 2010,11,12,12,12,12 )
console.log(date);
//参数为年、月、日等多个整数时,年和月是不能省略的,其他参数都可以省略的。 至少需要两个参数,因为如果只使用“年”这一个参数,Date会将其解释为毫秒数。
得到六月一日
js
let d2 = new Date( 2020, 5, 1 ); // 不算时区
let d3 = new Date( '2020-06-01' ); // 算时区,8点
console.log(d2);
console.log(d3);
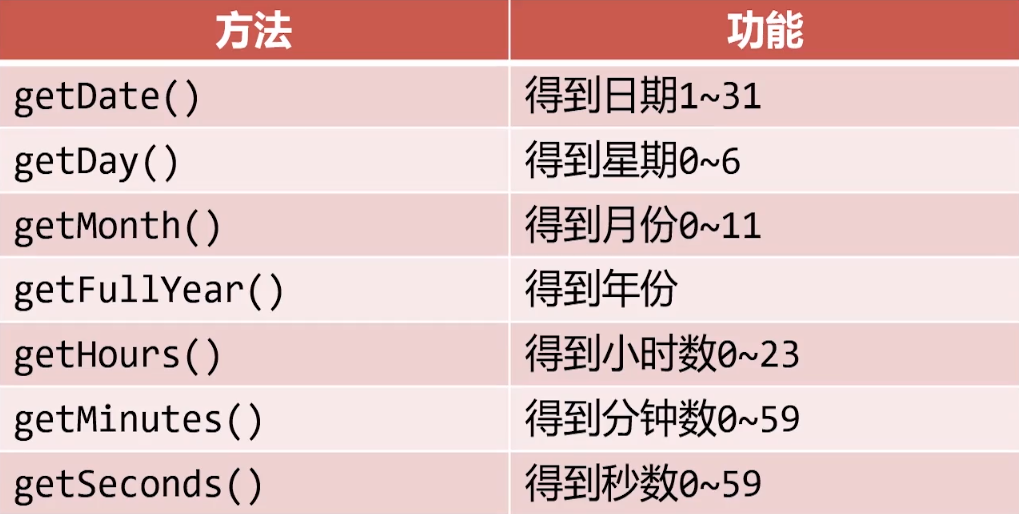
日期对象的常见的方法
js
let d = new Date();
console.log("日期" , d.getDate());
console.log("星期" , d.getDay());
console.log("年份" , d.getFullYear());
console.log("月份" , d.getMonth() + 1);
console.log("小时" , d.getHours());
console.log("分钟" , d.getMinutes());
console.log("秒数" , d.getSeconds());
时间戳
时间戳表示1970年1月1日零点整距离某时刻的毫秒数
通过getTime()方法或者Date.parse()函数可以将日期对象变为时间戳
js
let d = new Date();
let timestamp1 = d.getTime(); // 精确到毫秒
//虽然是对象,但是可以做减法
//(两个日期对象或者日期对象和数字都可以做减法)
console.log( d - 0 ); //减去0相当于调用getTime();
let timestamp2 = Date.parse(d); // 精确到秒,也是毫秒数,只不过最后三位一定是000
console.log(timestamp1);
console.log(timestamp2);
// 如何把时间戳,比如1601536565000变回日期对象呢?
let dd = new Date(1601536565000);
console.log(dd);
console.log(dd.getFullYear());
使用时间对象进行节流
js
let time = 0;
if(new Date() - time < 1000) return;
time = new Date();
小案例:时钟
html
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
ul {
list-style: none;
}
#wrap {
width: 400px;
margin: 200px auto;
/*border: 1px solid red;*/
user-select: none;
}
#wrap ul {
display: flex;
}
#wrap li {
margin: 0 3px;
}
#wrap .time {
/*background-color: pink;*/
transition: top 0.3s;
}
#wrap li:not(.dot) {
width: 100%;
height: 62px;
background: linear-gradient(to bottom, #434343 50%, #393939 50%);
border-radius: 10px;
line-height: 62px;
text-align: center;
color: #fff;
font-size: 26px;
}
#wrap .dot {
width: 20px;
height: 62px;
line-height: 62px;
text-align: center;
font-size: 26px;
font-weight: bolder;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="wrap">
<ul>
<li class="hours">0</li>
<li class="hours">0</li>
<li class="dot">:</li>
<li class="minutes">0</li>
<li class="minutes">0</li>
<li class="dot">:</li>
<li class="seconds">0</li>
<li class="seconds">0</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
let aLi = document.querySelectorAll("#wrap li:not(.dot)");
//变化函数
function fn() {
let date = new Date();
/*获取时分秒*/
let h = date.getHours().toString().padStart(2,0);
let m = date.getMinutes().toString().padStart(2,0);
let s = date.getSeconds().toString().padStart(2,0);
let str = h + m + s;
console.log(str);
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
aLi[i].innerHTML = str[i];
}
}
fn();
setInterval(fn , 1000);
/*个位补0*/
function toTwo(number) {
return (number < 10 ? "0" : "") + number;
/*if(number < 10){
return "0" + number;
}else{
return number + "";
}*/
}
// console.log(toTwo(1));
</script>
小案例:倒计时小程序
题目:在页面上实时显示距离2021年高考还有多少天、多少时、多少分、多少秒
html
<body>
<h1>2021年高考倒计时</h1>
<h2 id="info"></h2>
<script>
let info = document.getElementById('info');
function fn(){
// 现在的日期
let nd = new Date();
// 目标的日期,5表示六月
let td = new Date(2021, 5, 7);
// 毫秒差
let diff = td - nd;
// 任务很简单,就是把diff换算为天、小时、分钟、秒
// 换算为多少天,除以一天的总毫秒数,不就是换算为多少天么
let day = parseInt( diff / (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24));
// 零多少小时呢??差的总毫秒数与1天的毫秒数的相除的余数,就是零头的毫秒数
let hours = parseInt( diff % (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) / (1000 * 60 * 60) );
// 零多少分钟呢??
let minutes = parseInt(diff % (1000 * 60 * 60 * 24) % (1000 * 60 * 60) / (1000 * 60));
// 零多少秒呢??
let seconds = parseInt(diff % (1000 * 60 * 60) % (1000 * 60) / 1000);
info.innerText = day + '天' + hours + '时' + minutes + '分' + seconds + '秒';
}
fn();
setInterval(fn, 1000);
</script>
</body>
时间戳转换时间
js
// 现在的日期
let nd = new Date();
// 目标的日期,5表示六月
let td = new Date(2020 , 10, 6);
let dValue = td - nd;
// 天 毫秒除以1000就是秒 1秒除以60就是分钟 一分钟除以60就是小时 一小时除以24就是天
let day = parseInt(dValue / 1000 / 60 / 60 / 24)
// 小时 除以等于总共剩余多少小时之后 还要 模 24 因为超过24小时之后已经可以用天来表示
let hours = parseInt(dValue / 1000 / 60 / 60 % 24)
// 分钟 dValue / 1000 / 60 等于总共剩余的多少分钟 还要 模60 所有大于60的用小时表示 低于60用分钟
let mins = parseInt(dValue / 1000 / 60 % 60)
// 秒 表示60以下的秒 60以上的秒已经用分钟表示了
let seconds = parseInt(dValue / 1000 % 60)
let timer = day + "天" + hour + "小时" + mins + "分钟" + seconds + "秒";
console.log(timer);
 tian~
tian~